THE AUTHOR OF THIS BLOG IS YONA MESHACK SHANNY
PUBLICATION DATE: JUNE 24, 2023
NAME OF PROJECT: YOMESHA 4TH PROJECT
TITLE OF PROJECT: LEARN HOW TO DESIGN A LOCAL AREA NETWORK IN 2023 BY YOMESHA
E-MAIL: shannyyona@gmail.com
WhatsApp PHONE NO: 0685046743
NAME OF BLOG: tztech-media.blogspot.com
MAIN PURPOSE OF THE AUTHOR:
- TO EDUCATION THE COMMUNITY ALL ABOUT THE WORLD OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
- WHAT ARE BENEFITS AND MISCHIEF OF THE WORD OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
- HOW TO OVERCOME DIFFERENT PROBLEMS CAUSED BY THE WORLD OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
INTRODUCTION
LEARN HOW TO DESIGN A LOCAL AREA NETWORK (LAN) 2023 BY YOMESHA
Today i want to teach you how do design your good Local Area Network (LAN) for your own purpose or use even for business issue
In order to know how to design your simple Local Area Network (LAN) your might first know the three important things such as what is computer network, types of computer network as well as the different network topologies.
let us start
Computer Network
Is a set of computers sharing
resources located on or provided by network nodes. Computers use common
communication protocols over digital interconnections to communicate with each
other. Computer networks may be classified by many criteria, including the
transmission media which is used to carry signals, bandwidth, and
communications protocols to organize networks traffic, the network size, the
topology, traffic control mechanisms, and organizational internet. Below are several types of computer network:
Types of Computer Network
Generally, networks are distinguished based on their geographical span. A network can be as small as distance between your mobile phone and its Bluetooth headphone and as large as the internet itself, covering the whole geographical world.
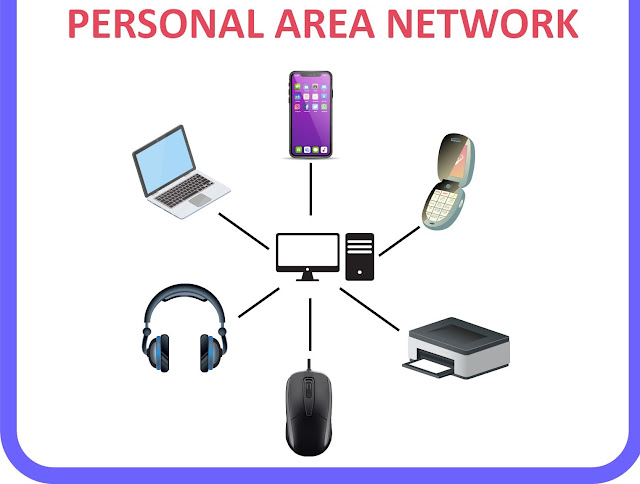
Personal Area Network
A Personal Area Network (PAN) is smallest network which is very personal to a user. This may include Bluetooth enabled devices or infra-red enabled devices. PAN has connectivity range up to 10 meters. PAN may include wireless computer keyboard and mouse, Bluetooth enabled headphones, wireless printers, and TV remotes.
For example, Piconet is Bluetooth-enabled Personal Area Network which may contain up to 8 devices connected together in a master-slave fashion.
Local Area Network
A computer network spanned inside a building and operated under single administrative system is generally termed as Local Area Network (LAN). Usually, LAN covers an organization offices, schools, colleges or universities. Number of systems connected in LAN may vary from as least as two to as much as 16 million.
LOCAL AREA NETWORK
 |
LAN works under its own local domain and controlled centrally.
LAN uses either Ethernet or Token-ring technology. Ethernet is most widely employed LAN technology and uses Star topology, while Token-ring is rarely seen.
LAN can be wired, wireless, or in both forms at once.
Metropolitan Area Network
The Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) generally expands throughout a city such as cable TV network. It can be in the form of Ethernet, Token-ring, ATM, or Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI). Metro Ethernet is a service which is provided by ISPs. This service enables its users to expand their Local Area Networks. For example, MAN can help an organization to connect all of its offices in a city.
METROPOLITAN AREA NETWORK
 |
- Web sites
- Instant Messaging
- Blogging
- Social Media
- Marketing
- Networking
- Resource Sharing
- Audio and Video Streaming
Ethernet is a widely deployed LAN technology. This technology was invented by Bob Metcalfe and D.R. Boggs in the year 1970. It was standardized in IEEE 802.3 in 1980. Ethernet shares media. Network which uses shared media has high probability of data collision.
Ethernet uses Carrier Sense Multi Access/Collision Detection (CSMA/CD) technology to detect collisions. On the occurrence of collision in Ethernet, all its hosts roll back, wait for some random amount of time, and then re-transmit the data.
Ethernet connector is network interface card equipped with 48-bits MAC address. This helps other Ethernet devices to identify and communicate with remote devices in Ethernet.
Traditional Ethernet uses 10BASE-T specifications. The number 10 depicts 10MBPS speed, BASE stands for baseband, and T stands for Thick Ethernet. 10BASE-T Ethernet provides transmission speed up to 10MBPS and uses coaxial cable or Cat-5 twisted pair cable with RJ-5 connector. Ethernet follows Star topology with segment length up to 100 meters. All devices are connected to a hub/switch in a star fashion.
ETHERNET
Fast-Ethernet
To encompass need of fast emerging software and hardware technologies, Ethernet extends itself as Fast-Ethernet. It can run on UTP, Optical Fiber, and wirelessly too. It can provide speed up to 100MBPS. This standard is named as 100BASE-T in IEEE 803.2 using Cat-5 twisted pair cable. It uses CSMA/CD technique for wired media sharing among the Ethernet hosts and CSMA/CA (CA stands for Collision Avoidance) technique for wireless Ethernet LAN. Fast Ethernet on fiber is defined under 100BASE-FX standard which provides speed up to 100MBPS on fiber. Ethernet over fiber can be extended up to 100 meters in half-duplex mode and can reach maximum of 2000 meters in full-duplex over multimode fibers.
FAST-ETHERNET
Giga-Ethernet
After being introduced in 1995, Fast-Ethernet retained its high speed status only for three years till Giga-Ethernet introduced. Giga-Ethernet provides speed up to 1000 mbits/seconds. IEEE802.3ab standardizes Giga-Ethernet over UTP using Cat-5, Cat- 5e and Cat-6 cables. IEEE802.3ah defines Giga-Ethernet over Fiber.
GIGA-ETHERNET
Virtual LAN
LAN uses Ethernet which in turn works on shared media. Shared media in Ethernet create one single Broadcast domain and one single Collision domain. Introduction of switches to Ethernet has removed single collision domain issue and each device connected to switch works in its separate collision domain. But even Switches cannot divide a network into separate Broadcast domains. Virtual LAN is a solution to divide a single Broadcast domain into multiple Broadcast domains. Host in one VLAN cannot speak to a host in another. By default, all hosts are placed into the same VLAN.
VIRTUAL LAN
In this diagram, different VLANs are depicted in different color codes. Hosts in one VLAN, even if connected on the same Switch cannot see or speak to other hosts in different VLANs. VLAN is Layer-2 technology which works closely on Ethernet. To route packets between two different VLANs, a Layer-3 device such as Router is required.
let us also go through several computer network topologies in brief:
A Network Topology is the arrangement with which computer systems or network devices are connected to each other. Topologies may define both physical and logical aspect of the network. Both logical and physical topologies could be same or different in a same network. Below are several computer network topologies:
Point-to-Point
Point-to-point networks contains exactly two hosts such as computer, switches, routers, or servers connected back to back using a single piece of cable. Often, the receiving end of one host is connected to sending end of the other and vice versa.
POINT-TO-POINT
If the hosts are connected point-to-point logically, then may have multiple intermediate devices. But the end hosts are unaware of underlying network and see each other as if they are connected directly.
Bus Topology
In case of Bus topology, all devices share single communication line or cable. Bus topology may have problem while multiple hosts sending data at the same time. Therefore, Bus topology either uses CSMA/CD technology or recognizes one host as Bus Master to solve the issue. It is one of the simple forms of networking where a failure of a device does not affect the other devices. But failure of the shared communication line can make all other devices stop functioning.
BUS TOPOLOGY
Both ends of the shared channel have line terminator. The data is sent in only one direction and as soon as it reaches the extreme end, the terminator removes the data from the line.
Star Topology
All hosts in Star topology are connected to a central device, known as hub device, using a point-to-point connection. That is, there exists a point to point connection between hosts and hub. The hub device can be any of the following:
- Layer-1 device such as hub or repeater
- Layer-2 device such as switch or bridge
- Layer-3 device such as router or gateway
- Full Mesh: All hosts have a point-to-point connection to every other host in the network. Thus for every new host n(n-1)/2 connections are required. It provides the most reliable network structure among all network topologies.
- Partially Mesh: Not all hosts have point-to-point connection to every other host. Hosts connect to each other in some arbitrarily fashion. This topology exists where we need to provide reliability to some hosts out of all.
- Transmission media: wired
- Network size: LAN
- Network topology: star topology
- RJ45 modular data plugs
This device is needed to crimp the RJ45 modular data plug
onto the wire making a connection on each of the pins of the data plug
3. Ethernet cable
This the device which is widely used for networking purpose
to establish wired connections between devices, but also Ethernet cable used to
create the local area network within home, schools and university and other
environments by multiple to a network switch or router using Ethernet cables user
can able to share files, printers, and other network resources.
4. Jacket\ sheath cutter\ or wire
stripper
This tool will safely cut the jacket off the wires inside without cutting
the wires. You will measure out about two inches of the cable to cut the jacket
off by twisting the cutter around the cable. This tool is often combined with
the RJ45 crimping tool.
5. Rubber shoe/ Rubber boot
They are designed to fit over the end the end of CAT-5 or CAT-6 connectors to relieve the strain on the connector and clean up the cosmetics of the cable this also improve the identification and durability of patch cords terminated with the industry standard RJ45 plug.
6. Computer
This is an electronic device accept input, store data, and provide output
when they are needed by the user. In the project computer are connected so as
to share some resources within the local area network such as printers and
Ethernet cable.
8. Switch
The main function of a switch filter and forward packets between local area network segments switch operate at the data link (layer 2) and sometime the network (layer 3) of the open system interconnect reference model and therefore support any protocol local area network that uses switch are called (switched local area network).
8. Extension
cable
This is a device used to supply electricity within the local area network. They are of several length but those which are much preferred are those which are long so that it could be easy to acquire the electricity even though the source is very far from the network.
9. Cable taster
This is an electronic device
used to verify the electronic connection in a signal cable or other wired assembly.
TERMINATION
Components:
RJ-45 connector.
Crimping Tool.
Twisted pair Cable.
rubber shoe.
cable striper.
STEP 1
By using a crimping Tool, you can trim the end of the cable that you want to terminating, to ensure that the ends of the conducting wires are even.
STEP 2
Careful we strip off approximately 1 inch of the cable's jacket, using a modular crimping tool or a wire stripper.
We separate the 4 twisted wire pairs from each other, and then unwind each pair, so that we end up with 8 individual wires. We flatten the wires out as much as possible, since they'll need to be very straight for proper insertion into the connector.
STEP 4
We arrange the wires in a flat, side-by-side ribbon formation, placing them in the following order: white orange, orange, white green, blue, white blue, green, white brown, and brown.
STEP 5
We hold the RJ45 connector so that its pins are facing away from us and the plug-clip side is facing down and then we carefully insert the flattened, arranged wires into the connector, pushing through until the wire ends emerge from the pins. For strength of connection, also push as much of the cable jacket as possible into the connector.
STEP 6
We check to make sure
that the wire ends coming out of the connector's pin side are in the correct
order.
STEP 7
We insert the prepared connector/cable assembly into the RJ45 slot in our crimping tool and firmly squeeze the crimper's handles together until we can't go any further and we release the handles and repeat this step to ensure a proper crimp.
STEP 8
This is
step that explain on how to verify the connection of wire if are arranged
properly and it involve to turn ON first the cable and then to insert the cable
which are already terminated.
STEP 9
After the completion of first termination, we repeat process on the opposite end of our cable and test the Ethernet.
NETWORK CONFIGURATIONS
On the server Computer
On the server computer, we are required to follow these
steps to share the network connection:
1.
Log in to the host computer as Administrator or as
Owner.
2.
Click on the search box then, search and open Control Panel.
3.
Select and click Network
and Internet.
4.
Select and click Network
and Sharing Center.
5.
Select and click Change
advanced sharing settings.
6.
Then turn ON
the following Network discovery, file
and printer sharing, public sharing folder, media streaming and password
protected sharing.
On the clients
Computer
On the client computer, we are required to follow these
steps to share the network connection:
1.
Log in to the client computer.
2.
Click on the search box then, search and open Control Panel.
3.
Select and click Network
and Internet.
4.
Select and click Network
and Sharing Center.
5.
Select and click Change
advanced sharing settings.
6.
Turn ON the
following Network discovery, file and
printer sharing, public sharing folder and password protected sharing then
turn OFF media streaming.
Procedure for creation workgroup
Ø
Go to start menu and press on search button
“change workgroup name”
Ø
Then open “change workgroup” click “change”
Ø
Give name to the computer.
Ø
Select workgroup and write the name of the
workgroup
Ø
Click “OK” then “apply”
Ø
Click “OK” on the required computer to restart
Ø
Then click “CLOSE” then “restart now”
This workgroup and computer
name helps to identify name of the computer shared in a network as well as
helps to organize all computer in a network to facilitate sharing resources.
Procedure for resource
sharing
a. File sharing
Ø
Select a folder that contain the file be shared
then right click and press on properties
Ø
Click on security then edit ,then add, the
advanced
Ø
Click find now and go to search now result then
find everyone.
Ø
Click “OK” then “OK” again.
Ø
Permit everyone then select full control then
apply then click ok.
Ø
Go to sharing, click share.
Ø
Click an arrow to find everyone then select
everyone then click add and give permission to read and write.
Ø
Then click share and done.
Ø
Go to advanced sharing and select share this
folder then click “Apply” and “OK”.
Ø
Then click close.
The file will be already
shared.
b. Printer sharing (Source
computer connected to printer).
Ø
Open the control panel.
Ø
Go to devices and printers sharing.
Ø
Then open, after opening select the printer
which connected to the computer.
Ø
Then right click on that printer and select
printer properties and click it.
Ø
Go to security then select everyone and on
permission for everyone, give the permission print.
Ø
Click sharing, then select this printer, then
apply and click OK.
We observed printer shared
on other on other computers in a network.
On other computers (That are not connected direct to printer).
Ø
Open the computer network.
Ø
Select the computer that shared the printer to
other computers in a network.
Ø
Select printer which is shared and open it, in order
to install.
Finally we observed shared printer is
stored in a computer and has permission to print now.
Procedures to assign IP address on a
selected computer.
Ø
Select and right click on a computer network,
then click properties.
Ø
Click “Change adapter setting”.
Ø
Select Ethernet and right click.
Ø
After that click “properties” and select
Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4).
Ø
Click properties then select “Use the following
IP address”.
·
We decided to use IP address class C which is
found in the range of 192.168.20.1 (for the first computer).
·
Click subnet mask, in which we observed the
subnet mask assigned automatic according to our class range.
Ø
Then click “OK”.
Ø
After assigning the IP address, we then opened
the command prompt in order to check our IP address which we assigned in our
computers.
Ø
Use ipconfig command to check the IP address and
subnet mask which are assigned.
Ø
Then use the ping command to ping the IP address
of the other computers connected in the same network, in order to check
connection if it is ok.
Ø
If it is OK, it displays the message reply and
if it is not OK, it displays the message “Time out”.
Overview


































.jpg)
0 comments: